INTRODUCTION
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that’s found in all the cells in your body. Your body needs some cholesterol to make hormones, vitamin D and substances that help you digest foods. Your body makes all the cholesterol it needs. But too much cholesterol can pose a problem. However, having high levels of cholesterol can increase your risk of heart disease.
Types
There are two main types of cholesterol:
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL)

Often called “bad” cholesterol, high levels of LDL can lead to plaque buildup in your arteries, which can narrow or block blood flow and increase the risk of heart attacks or strokes.
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
Known as “good” cholesterol, HDL helps remove LDL cholesterol from your bloodstream, thus reducing the risk of heart disease.
SYMPTOMS
High cholesterol has no symptoms. A blood test is the only way to detect if you have it.
Impact of High Cholesterol on your Health
Here’s how high cholesterol can impact your health and what to look out for:
- Heart Disease: High cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which may cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or in severe cases, a heart attack.
- Stroke: Atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries) due to high cholesterol can also affect the brain’s blood vessels, potentially leading to a stroke. Symptoms of a stroke include sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body, confusion, trouble speaking, or severe headache.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): High cholesterol can cause narrowing of the arteries in the legs, which may lead to pain, cramping, or weakness in the legs during physical activity.
- Xanthiums: In rare cases, very high cholesterol levels can cause fatty deposits to form in the skin or tendons, known as xanthiums.
PREVENTION
The same heart-healthy lifestyle changes that can lower your cholesterol can help prevent you from having high cholesterol in the first place. To help prevent high cholesterol, you can:
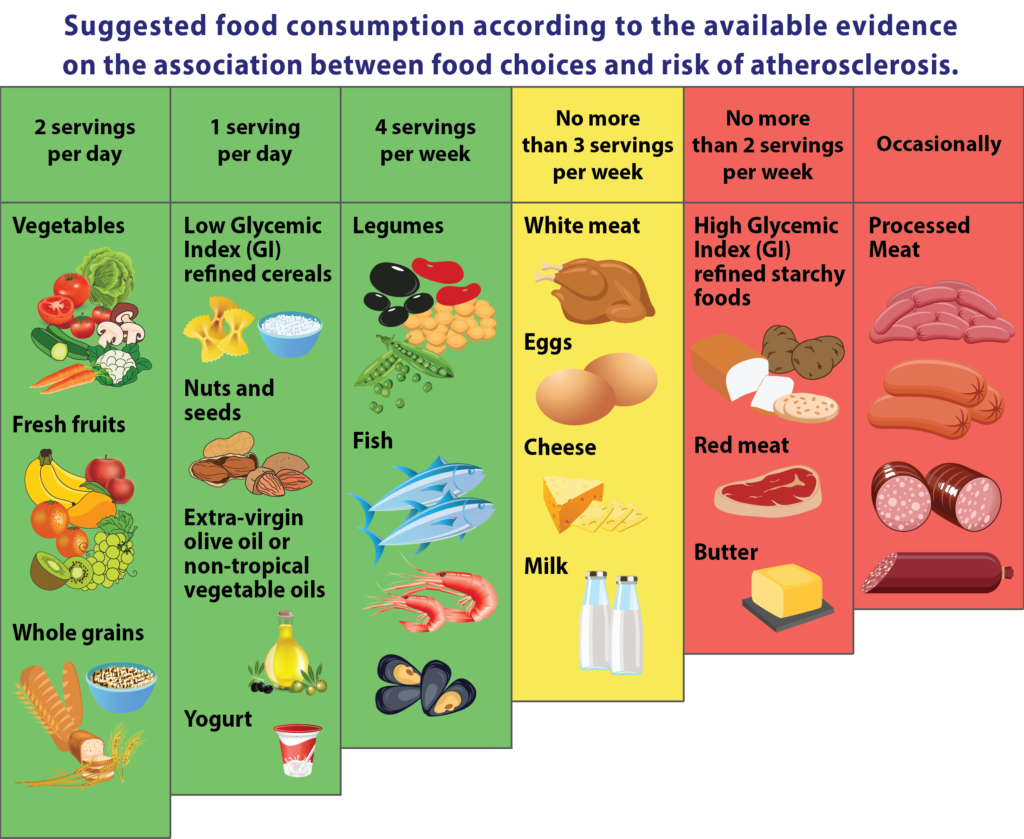
- Eat a low-salt diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables and whole grains
- Limit the amount of animal fats and use good fats in moderation
- Lose extra fat and maintain a healthy weight
- Quit smoking
- Exercise on most days of the week for at least 30 minutes
- Manage stress
MEDICATION
Herbal medications and supplements can play a role in managing cholesterol levels, though they should be used in conjunction with, not as a replacement for, conventional treatments and lifestyle changes. Here are some commonly used herbs and supplements that may help support healthy cholesterol levels:
1. Garlic
Garlic has been shown to potentially lower LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
2. Green Tea
Rich in antioxidant, green tea may help reduce LDL cholesterol and improve heart health.
3. Flaxseed
Flaxseeds are high in omega-3 fatty acids and soluble fiber, which may help lower LDL cholesterol.
4. Niacin (Vitamin B3)
Niacin can help increase HDL cholesterol and lower LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
5. Red Yeast Rice
Contain compounds similar to statin medications, which can help lower LDL cholesterol.
6. Guggul
Derived from the resin of the Commiphora wightii tree, guggul may help lower LDL cholesterol and triglycerides..
7. Red Clover
Contain compounds that may help improve cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
8. Berberine
Found in several plants, berberine may help lower LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
Important Considerations
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Before starting any herbal supplements, especially if you are taking medications or have health conditions, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions or side effects.
- Quality Matters: Choose high-quality supplements from reputable sources, as the potency and purity can vary.
- Complementary Approach: Use herbal supplements as a complementary approach alongside conventional treatments and lifestyle changes for the best results.
This Article is for Basic Information. Contact a professional doctor before using it.
HAKEEM KARAMAT ULLAH
+923090560000