Introduction

Cinnamon, known as Dar Chini in many South Asian cultures, is a beloved spice that has been cherished for centuries not only for its aromatic flavor but also for its numerous health benefits. Derived from the inner bark of trees in the Cinnamomum genus, cinnamon is widely used in cooking, baking, and traditional medicine. It comes in two main varieties: Ceylon cinnamon, known as true cinnamon, and Cassia cinnamon, which is more commonly found in stores. While both types offer a range of health benefits, it’s important to be aware of their potential side effects, especially with overconsumption. Cinnamon is rich in antioxidants, possesses anti-inflammatory properties, and may help regulate blood sugar, making it a popular natural remedy for managing conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and digestive issues. However, excessive consumption, particularly of Cassia cinnamon, can lead to adverse effects, including liver damage and digestive discomfort. In this article, we explore the many benefits of cinnamon, as well as the potential risks associated with its use.
Forms
Cinnamon is available in several forms, each serving different purposes in cooking, baking, and medicinal uses. The various forms of cinnamon allow for flexibility in how it is used in the kitchen and for health benefits.

- These are whole pieces of cinnamon bark, often rolled up into cylindrical shapes. Cinnamon sticks are commonly used to infuse flavor into liquids such as tea, coffee, soups, and stews. They can also be used in homemade potpourri or as a decorative garnish.
Ground Cinnamon (Powdered Cinnamon): - Ground cinnamon is the most commonly used form. It is made by grinding the cinnamon sticks into a fine powder. Ground cinnamon is versatile, used in baking, cooking, and as a topping for oatmeal, smoothies, or even coffee. It is readily available in most grocery stores.
Cinnamon Oil: - Cinnamon essential oil is extracted from the bark or leaves of the cinnamon tree. It has a potent aroma and is used in aromatherapy for its calming and anti-inflammatory properties. Cinnamon oil is also used in cosmetics and skin care for its antibacterial and antifungal benefits. However, it should be used with caution as it is very concentrated and may cause irritation if applied directly to the skin.
Cinnamon Extract: - This is a concentrated form of cinnamon, often used for its medicinal benefits. Cinnamon extract is made by soaking cinnamon in alcohol or glycerin, extracting the active compounds. It is typically used in supplements or as a natural remedy for issues like blood sugar regulation and digestive health.
Cinnamon Tea: - Cinnamon can be used to make tea by steeping cinnamon sticks or adding ground cinnamon to hot water. This is a soothing drink commonly consumed for its warming properties and potential health benefits, such as aiding digestion and reducing inflammation.
Cinnamon Honey - Cinnamon honey is a mixture of cinnamon powder and honey, often consumed for its potential health benefits. It combines the antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties of cinnamon with the soothing and healing qualities of honey. The combination is believed to boost immunity, aid digestion, regulate blood sugar, and improve skin health
Cinnamon Capsules - Cinnamon capsules are dietary supplements containing either ground cinnamon powder or cinnamon extract. These capsules are taken for their potential therapeutic benefits, particularly for managing blood sugar levels, improving heart health, and reducing inflammation.
Health Benefits of Cinnamon (Dar Chini)
Cinnamon is more than just a flavorful spice; it has been valued for centuries for its medicinal properties. Below are some of the key health benefits associated with cinnamon:
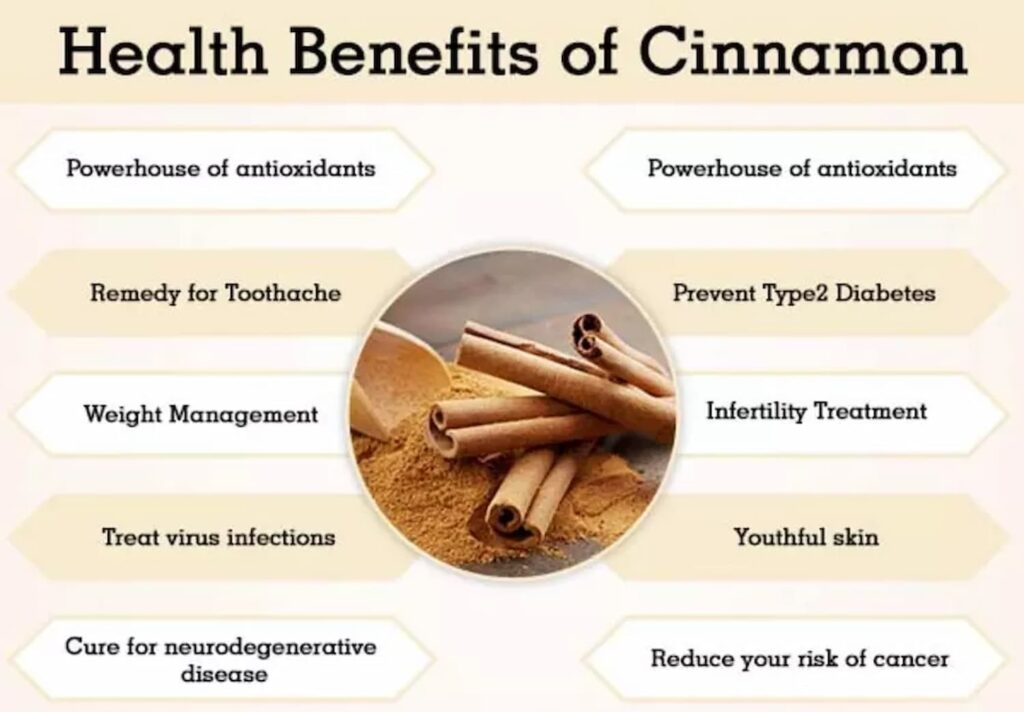
- Rich in Antioxidants:
- Cinnamon is loaded with powerful antioxidants, such as polyphenols, which help protect the body from oxidative stress and inflammation. These antioxidants help reduce the risk of chronic diseases by neutralizing free radicals in the body.
- Cinnamon is loaded with powerful antioxidants, such as polyphenols, which help protect the body from oxidative stress and inflammation. These antioxidants help reduce the risk of chronic diseases by neutralizing free radicals in the body.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties:
- The active compounds in cinnamon, like cinnamaldehyde, possess potent anti-inflammatory effects. Regular consumption may help reduce inflammation in the body, which is a contributing factor to many chronic conditions like arthritis and heart disease.
- The active compounds in cinnamon, like cinnamaldehyde, possess potent anti-inflammatory effects. Regular consumption may help reduce inflammation in the body, which is a contributing factor to many chronic conditions like arthritis and heart disease.
- Supports Heart Health:
- Cinnamon has been shown to reduce levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, while increasing “good” HDL cholesterol. This can improve overall heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases like heart attack and stroke.
- Cinnamon has been shown to reduce levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, while increasing “good” HDL cholesterol. This can improve overall heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases like heart attack and stroke.
- Regulates Blood Sugar:
- One of cinnamon’s most well-known benefits is its ability to help regulate blood sugar levels. Cinnamon can improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to process glucose. This is particularly beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
- One of cinnamon’s most well-known benefits is its ability to help regulate blood sugar levels. Cinnamon can improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to process glucose. This is particularly beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
- Improves Digestive Health:
- Cinnamon has been traditionally used to aid digestion. It can help relieve indigestion, bloating, and gas. Its antimicrobial properties also assist in combating harmful bacteria and fungi in the digestive tract, which may contribute to digestive issues.
- Cinnamon has been traditionally used to aid digestion. It can help relieve indigestion, bloating, and gas. Its antimicrobial properties also assist in combating harmful bacteria and fungi in the digestive tract, which may contribute to digestive issues.
- Antimicrobial Effects:
- Cinnamon has natural antimicrobial properties, helping to fight off bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It has been used in traditional medicine to treat infections and improve oral hygiene by reducing harmful bacteria in the mouth.
- Cinnamon has natural antimicrobial properties, helping to fight off bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It has been used in traditional medicine to treat infections and improve oral hygiene by reducing harmful bacteria in the mouth.
- Brain Health and Cognitive Function:
- Some studies suggest that cinnamon can help protect the brain against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. The spice may also enhance cognitive function, improve memory, and support overall brain health.
- Some studies suggest that cinnamon can help protect the brain against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. The spice may also enhance cognitive function, improve memory, and support overall brain health.
- Weight Loss Aid:
- Cinnamon may aid in weight loss by helping to regulate blood sugar levels, which can reduce cravings and improve fat metabolism. It can also boost metabolism and promote fat-burning.
- Cinnamon may aid in weight loss by helping to regulate blood sugar levels, which can reduce cravings and improve fat metabolism. It can also boost metabolism and promote fat-burning.
- Helps Fight Infections:
- The antibacterial and antifungal properties of cinnamon make it effective against a variety of infections, including those caused by bacteria like E. coli and fungi like Candida. It has been used in traditional medicine for centuries to treat colds, coughs, and infections.
- The antibacterial and antifungal properties of cinnamon make it effective against a variety of infections, including those caused by bacteria like E. coli and fungi like Candida. It has been used in traditional medicine for centuries to treat colds, coughs, and infections.
- Improves Skin Health:
- Cinnamon’s anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties make it beneficial for skin health. It can help reduce acne, soothe skin irritation, and promote a healthy complexion. When used topically, cinnamon can improve blood circulation and promote skin rejuvenation.
- Cinnamon’s anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties make it beneficial for skin health. It can help reduce acne, soothe skin irritation, and promote a healthy complexion. When used topically, cinnamon can improve blood circulation and promote skin rejuvenation.
- Boosts Immunity:
- Due to its antimicrobial, antiviral, and antioxidant properties, cinnamon can help strengthen the immune system, making it easier for the body to fend off infections and diseases.
Side Effects of Cinnamon (Dar Chini)

- Liver Damage (Cassia Cinnamon)
- Allergic Reactions
- Low Blood Sugar
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Risk During Pregnancy
- Mouth and Throat Irritation
- Interference with Medications
This Article is for Basic Information. Contact a professional doctor before using it.
HAKEEM KARAMAT ULLAH
+923090560000




